In today’s digital age, websites and web applications often rely on databases to store and manage data. MySQL database is a popular relational database management system used by many developers and website administrators. This step-by-step tutorial will guide you through the process of setting up a MySQL database and user using cPanel, a widely used hosting control panel.

Table of Contents
What is MySQL Database
MySQL is an open-source relational database management system (RDBMS) that is widely used for managing and organizing data. It is a key component in the LAMP (Linux, Apache, MySQL, PHP/Perl/Python) and MERN (MongoDB, Express.js, React, Node.js) stacks, which are popular choices for developing web applications.

Key features of MySQL
- Relational Database Management System (RDBMS): MySQL follows the relational database model, where data is organized into tables with rows and columns. Tables can be related to each other through keys, establishing relationships.
- Structured Query Language (SQL): MySQL uses SQL, a standard language for managing and manipulating relational databases. This allows users to perform tasks such as querying, updating, inserting, and deleting data.
- Open Source: MySQL is open-source software, which means that its source code is freely available and can be modified and redistributed. This has contributed to its widespread adoption and a large community of developers and users.
- Cross-Platform Compatibility: MySQL is designed to be cross-platform, meaning it can run on various operating systems, including Linux, Windows, and macOS. This flexibility makes it a versatile choice for different environments.
- Scalability: MySQL can handle both small and large databases, making it suitable for a wide range of applications. It supports the partitioning of tables, which helps distribute large datasets across multiple storage devices.
- Performance: MySQL is known for its high performance, especially in read-intensive operations. It employs various optimization techniques to enhance query execution and response times.
- Security: MySQL provides robust security features, including access control mechanisms, encryption options, and user authentication. It allows administrators to define user privileges and restrict unauthorized access to sensitive data.
- Community Support and Documentation: MySQL has a large and active community of developers and users. This community support, along with comprehensive documentation, makes it easier for users to find solutions to issues and stay updated on best practices.
Steps to create the database in cPanel
Creating a database in cPanel is a straightforward process. Here are the steps to create a MySQL database using cPanel:
Login to cPanel
- Open your web browser and navigate to the cPanel URL provided by your hosting provider.
- Enter your cPanel username and password to log in.
Locate MySQL Databases
In the cPanel dashboard, look for the “Databases” section. It is often represented by an icon labeled “MySQL Databases” or a similar name.
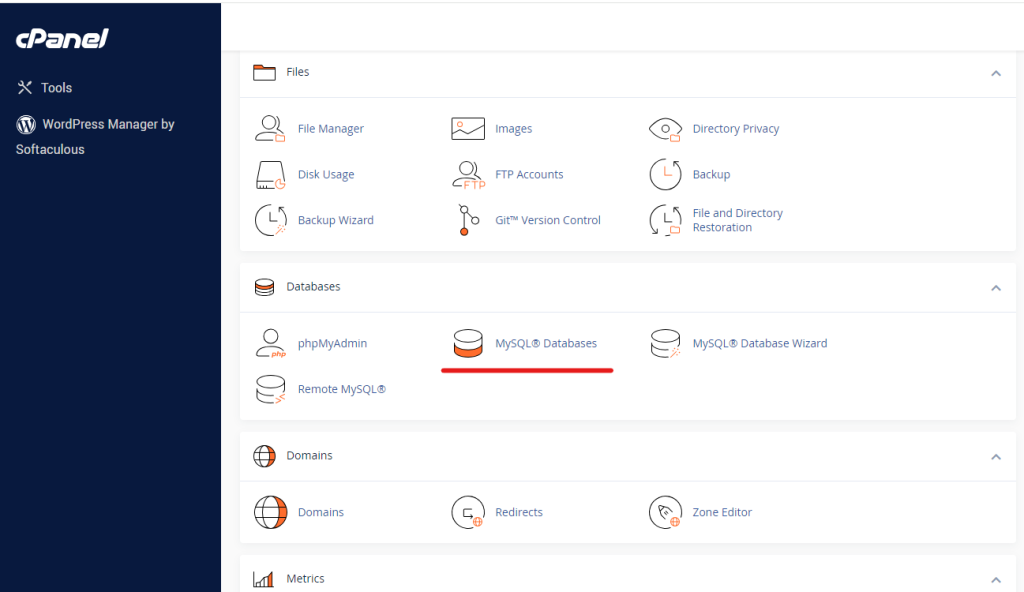
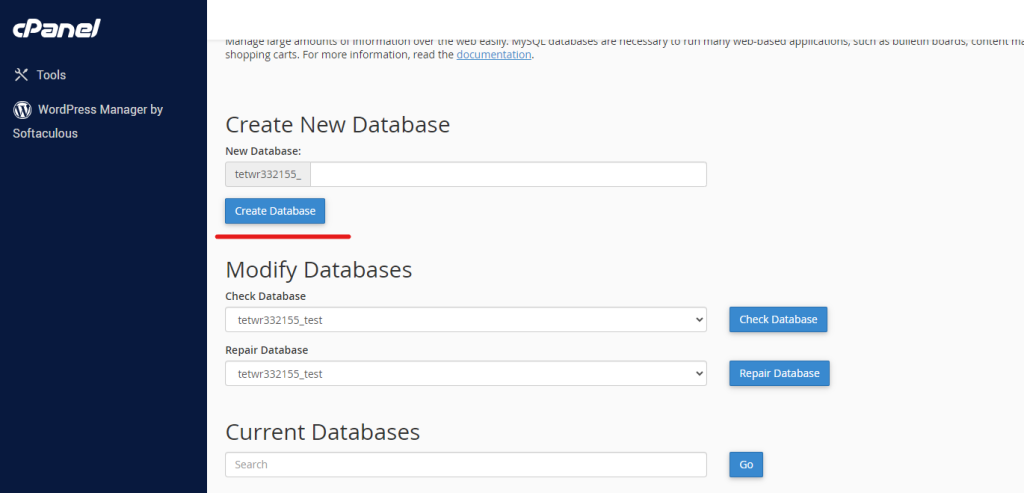
Create a New Database
- Within the MySQL Databases section, find the option to “Create New Database.”
- Choose a name for your database. The database name will be prefixed with your cPanel username for identification.
- Click the “Create Database” button to complete the creation of the database.
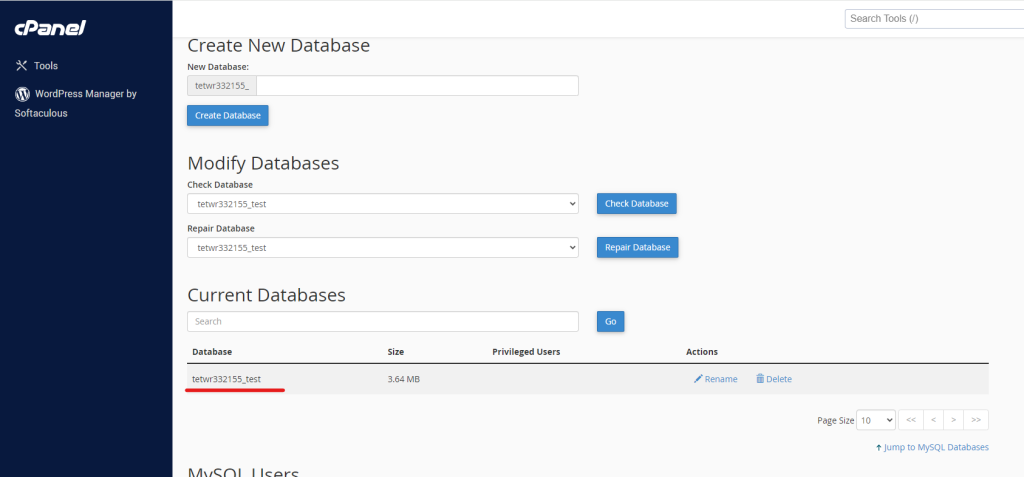
Add a Database User
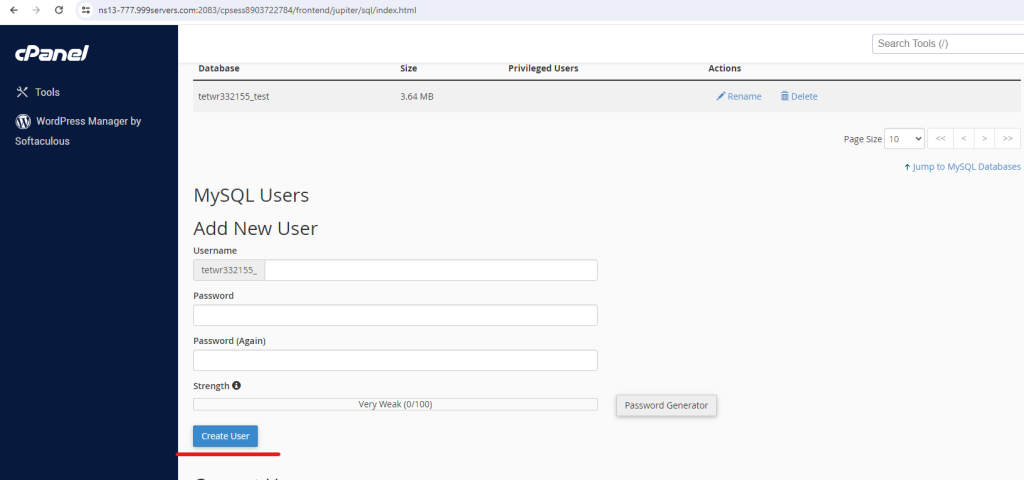
- Scroll down to the “MySQL Users” section.
- Create a new user by entering a username and a strong password.
- Click the “Create User” button.
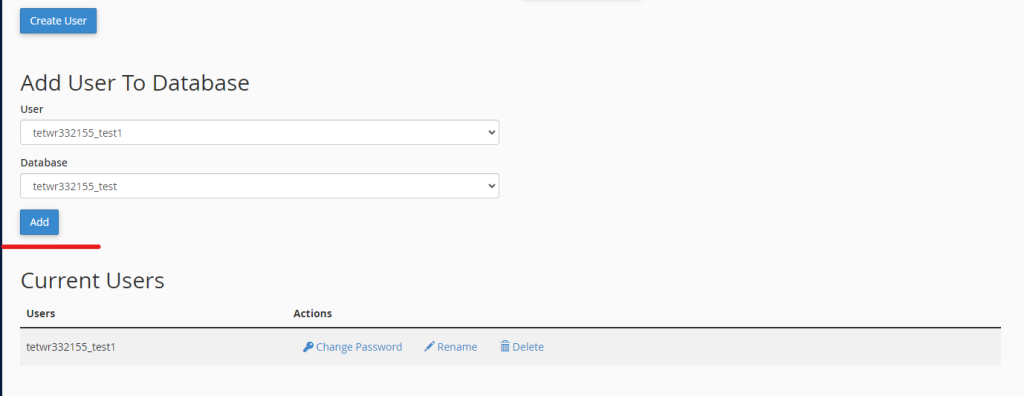
Assign User to Database
- In the MySQL Users section, find the “Add User to Database” option.
- Select the user you created and the database you created earlier.
- Click the “Add” button to link the user to the database.
Conclusion
Setting up a MySQL database and user in cPanel is an essential skill for managing web applications and websites. This tutorial has walked you through the process, from creating a database to setting up a user and configuring privileges. With this knowledge, you are better equipped to manage and optimize your database-driven projects efficiently.

